Statements
Adaptive Script allows you to execute one or more statements, sequentially.
Statements are separated by the ; character. This programmatic flow lets the
programmer write logic procedurally. The following is a list of the
statements that are available in Adaptive Script.
Block

A Block is a sequence of statements that are executed sequentially. When
creating a script, a new block is created initially. Blocks can be nested
inside existing blocks, using braces { }.
Example
{
let x = 1;
let y = 2;
let z = x + y;
print(z);
}Assignment

The Assignment statement assigns the value of an Expression to an AssignmentExpression. An AssignmentExpression is also an Expression which must evaluate to one of the following:
- VariableReference
- ReferenceByIndex
- ReferenceByName
This flexibility allows us to support a popular technique of assignment known as "destructuring". In destructuring, we assign an object or list into multiple variable names in one assignment.
Example
let x = 1;
let {y} = { y: 2 };
let [z] = [ 3 ];Break
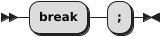
The break statement breaks out of the current block.
Example
while (true) {
if (1 < 2) {
break;
}
}Call

A Call statement is an evaluation that compiles to the call of an Adaptive Value.
Const

The const statement declares constant variables.
Example
const x = 1;Declare

Do While

The do-while statement executes a block of statements until a condition is met. Unlike the while statement, the do-while statement executes at least once.
Example
let x = 0;
do {
x = x + 1;
} while (x < 10);For
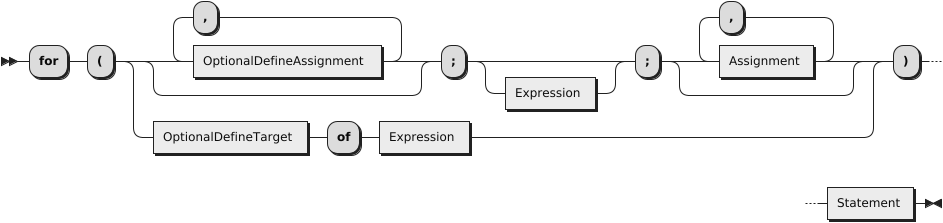
The for statement executes a block of statements
until a condition is met. Unlike the while statement, the for
statement executes an initializer, a condition, and an incrementor.
Example
for (let i = 0; i < 10; i = i + 1) {
print(i);
}Foreach

Example
foreach let x of [1, 2, 3] {
print(x);
}Function

This declares a function.
Example
function func(a, b) {
return a + b;
}
function func2(a, b) : a + b;If

The if statement executes a block of statements
if a condition evaluates to true.
Example
if (1 < 2) {
print(1);
}Interface
Let
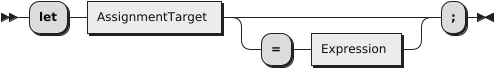
The let statement declares a local variable.
let x = 1;Return

The return statement returns a value from a
block of execution.
Example
function func(a, b) {
return a + b;
}Switch

The switch statement branches control flow based
on the value of an expression and the value of each case.
Example
switch (val) {
case 1:
print(1);
break;
case 2:
print(2);
break;
default:
print("default");
break;
}
Unlike the switch in ECMAScript, Adaptive Script
includes an optional syntax that allows you to specify a matching
function through the using option. The function
provided must take two values and return a boolean result. You may
use any built-in Adaptive Function, or provide a custom function,
written in Adaptive Script.
Example
switch ("abc") using regexp_match {
case "a.*":
// do something
break;
default:
// no match
break;
}Type

While

The while statement executes a block of
statements until a condition is met. Unlike the do-while statement,
the while statement executes the condition first and may not
execute the block at all.
Example
while (false) {
print("This won't execute!");
}